Important Events in Art From 1000 Ad to 1600 Ad Important Markings of Art in 1000 Ad
Graphic pattern is and then much a part of our modern earth that information technology is hard to imagine living without it. And in some ways, we never have: visual communication is about as one-time as our opposable thumbs, though information technology's been a long journeying from stone tools to digital tablets. In short, the history of graphic blueprint is a story that spans the entirety of human existence and it has the power to inspire and inform even mod graphic designers.
For one thing, knowing where, why and how this manufacture came about helps designers understand their place alongside history. In more practical terms, stylistic trends are cyclical, and studying the by can inspire some innovative ideas in the present. So bring together the states as we trace the roots of design from pre-industrial history into the industry we know today. With whatsoever luck, you lot might just leave your ain footprint along the style!

- Earlier the Printing Press: Prehistory to the Renaissance
- Cave paintings
- Sumerian written language
- Chinese press
- Medieval calligraphy
- European heraldry
- Storefronts
- The birth of graphic blueprint: Renaissance and Industrial Era
- Gutenberg press
- First logos
- Commencement Print Advertisements
- Chromolithography
- Graphic design in the modern era
- The Wiener Werkstätte
- Paul Rand
- A glimpse into the digital era
- The history of graphic design is ongoing
Earlier the printing press: Prehistory to the Renaissance
—
Graphic design proper really began afterward the invention of the printing press in 1440, but the roots of visual communication stretch all the way back to caveman times. In this section, we'll run downwardly the events of early history that paved the way for graphic design centuries before the world was ready for information technology.
Cave paintings ~38,000 BCE
It seems like humans have e'er had an inherent drive towards art, evidenced by the early on cavern paintings dating back to prehistoric times. Subjects vary from animals to hand imprints to events like hunting, and they've been establish all over the world (Australia, Spain, Republic of indonesia, France, Argentina, only to name a few). Historians debate the fine details as to who these were meant to communicate with (whether each other or their gods), just 1 thing that'southward clear is, correct from the get-go, humanity displayed a knack for communicating with visuals.

Sumerian written linguistic communication – 3300 – 3000 BCE
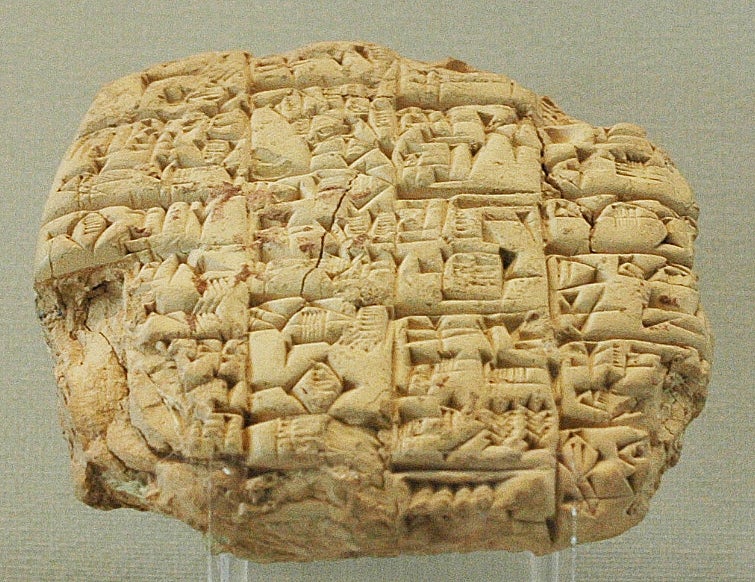

Every bit you read this article, interpreting all these tiny, abstract marks of the Latin Alphabet into words and sentences, it's easy to forget that alphabets are a human-made invention. As far as we know, the Sumerians created one of the first written languages, almost likely equally a means of recording trader inventories to ensure couriers didn't steal annihilation on deliveries.
These earliest languages were logographic—icons represented entire words instead of phonetic sounds. This suggests a natural power of humans to use visual representation to communicate complex ideas, a cornerstone of modern graphic design. And in the terminal few millennia, not much has changed: designers nevertheless rely on icons like hamburger menus or magnifying spectacles to represent entire words and concepts in limited space.
Advancements in Chinese printing 200 CE – 1040 CE

China holds most of the records for printing discoveries, including non-papyrus paper making, woodblock printing, and movable blazon—all of which occurred earlier than you might have guessed.
As far dorsum every bit 200 CE, Red china used wood reliefs to print and stamp designs on silk clothes, and later paper. In 1040, Bi Sheng invented the world'due south commencement movable type printing press out of porcelain, more 400 years before Gutenburg brought a similar engineering science to Europe.
Medieval calligraphy – 700s
In the Middle Ages, typography started to take off as humanity started expanding its aesthetic horizons into the letters and words themselves. Because texts in this catamenia were produced and replicated past paw, a little artistry made the books more than valuable and set sure scholars apart from others. In Islamic cultures, typography was doubly important considering figurative art was seen as sacrilegious, meaning typography was i of but a few permissible ways of artistic expression.
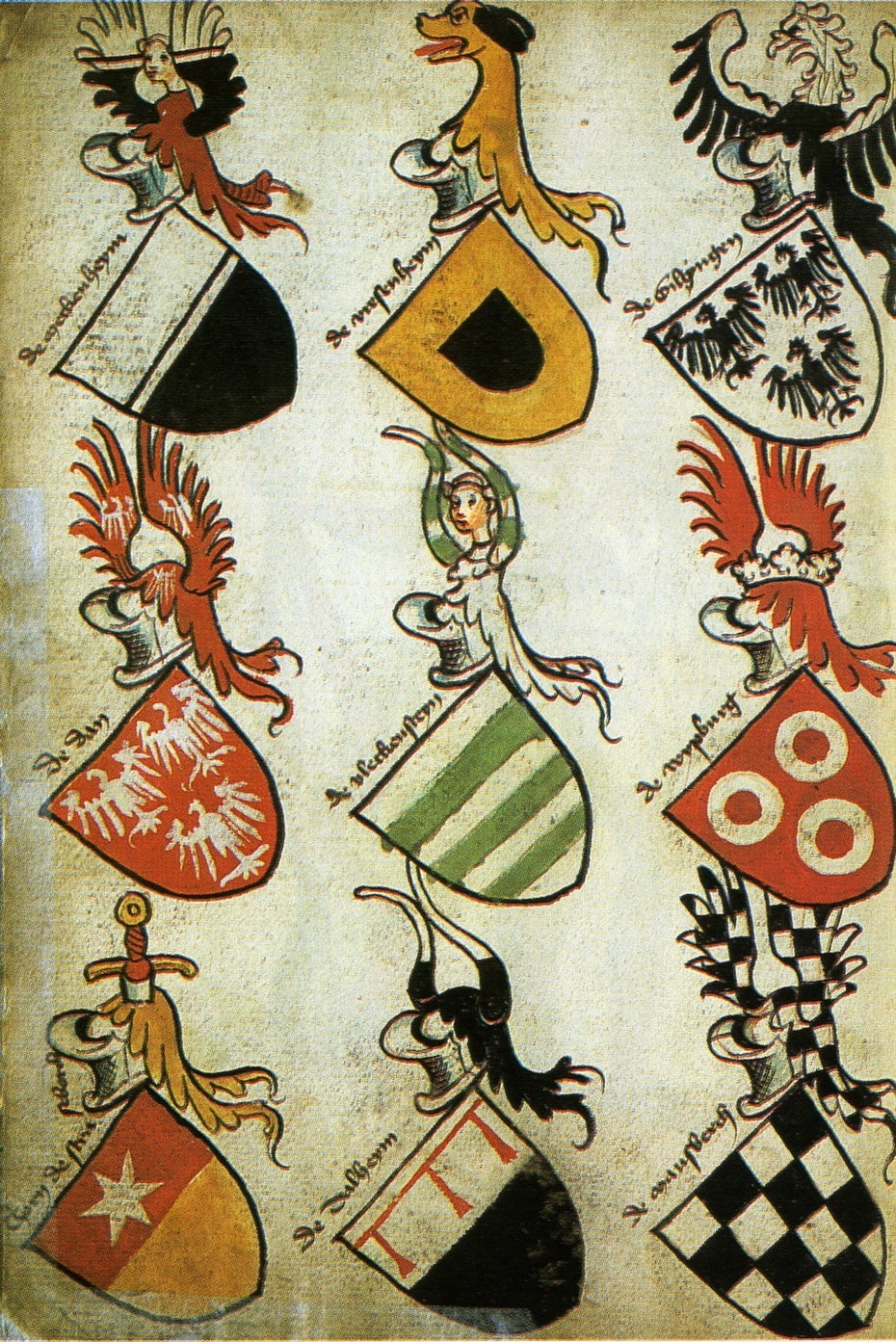


European heraldry – ~1100
Technically, the world's first logo is the coat of artillery, used as a symbol to represent family houses or territories. Scholars theorize the practice was popularized during the Crusades, where intermingling soldiers from dissimilar countries and houses incentivized a means to tell anybody autonomously, particularly on armor and battle flags.
Like logos, a house's coat of artillery aimed to represent the values, characteristics and styles of the people. Later, these emblems took on more applied purposes, such as wax seals to reflect authenticity.
Storefront signage – 1389

In the 14th century, beer and ale were viable if not preferable alternatives for drinking water at a time when most water sources were polluted. King Richard 2 of England fabricated a law that ale houses must have signs out front and so the public could find them easier.
Not but were these the showtime signage that actually represented companies rather than houses, but they're likewise the origin of a cute tradition that survives to this twenty-four hour period.
The birth of graphic design: Renaissance and Industrial Era
—
With the appearance of the printing press in Europe, humanity was able to recreate text, art and design on a massive scale, and for relatively cheap. The ancestors of modern companies—also on the rise—before long took notice of how such visuals could affect shopping behaviors and increase profits, thus modern graphic design was born.

Invention of the Gutenberg press – 1439
Johannes Gutenberg brought moveable type to Europe in 1439, introducing mass advice to Western culture and forever changing civilization. With the Gutenberg printing, people no longer had to rely on lengthy scholarly reproductions of books, opening up literature (and literacy) to the masses and making it affordable. The Gutenberg press paved the way for more than commercial uses of blueprint, which ushered in the era of graphic design as we know it.

Start logos – late 1400s
It was the printing industry that first used logos, although they were express to simply marks on their own documents. It wasn't simply a branding device, but too a means to testify off your printing skill—how well your logo was printed reflected how well everything was printed.

First print advertisements – 1620s
The press printing gave mode to the "coranto," the forerunner to the newspaper. And in the early 1600s, these corantos featured the first printed advertisements.
(To be fair, written advertisements date back to ancient Arab republic of egypt, only this is the first time we see images in mass-produced ads.)
Chromolithography – 1837
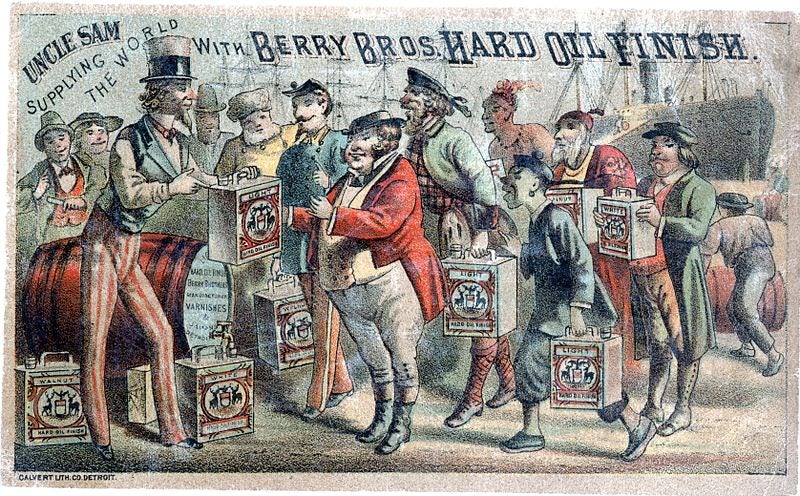

Technological advancements continued to fuel the progression of graphic pattern, such every bit the power to print in color, or chromolithography. While used primarily for recreating paintings for habitation decor, chromolithography also opened new doors for advertising.

Brands were now able to use a lot of the familiar marketing tools we know today, such as characteristic color schemes and building emotional connections through slice-of-life scenes. Before, visuals were stilted by the tech of the time (run across the ink absorb coranto prototype in the previous section) and prioritized bones clarity instead of touching on complex emotions. But chromolithography enabled some degree of realism, allowing advertizement to capitalize on attractive models, fashions of the mean solar day and creative usage of colors.
Graphic design in the modern era
—
Graphic design as we know it today really started developing in the modern era, roughly the belatedly 1800s up until the end of World State of war II. While the 19th century was more than about technological advancements and new capabilities, the modern era was about learning how to exploit these advancements for more creative aims. With printing at present a common tech and contest fueling innovation, artists and designers were pushed to explore new styles and techniques, which apace trickled into advertising and branding.
The Wiener Werkstätte (first graphic design agency) – 1903
With more and more companies recognizing the benefit of graphic pattern, it was just a matter of time before the starting time graphic pattern agency emerged. That honour belongs to Austria's Wiener Werkstätte, an organisation who made contributions to blueprint mode and business alike.

Meaning only "Vienna workshop," the Wiener Werkstätte was the first such organization of visual artists, including painters, architects, and early graphic designers. Organizationally, it set the precedent for all other collaborative agencies to follow.
Perhaps its greatest legacy was stylistic innovation, such as cubism. And as a grouping of professional artists working together, they held great influence over establishing pattern standards for upcoming generations of artists, particular those after World War I when cultural attitudes were changing worldwide. The work done at the Wiener Werkstätte set the stage for the popular Bauhaus and Art Deco styles that before long followed.
Staatliches Bauhaus founded – 1919

Furthering what the Wiener Werkstätte started, the Staatliches Bauhaus, or just simply "Bauhaus," first opened its doors in Weimar, Deutschland in 1919. Theirs was an ambitious goal: to create a Gesamtkunstwerk, an artistic ideal that encompasses or synthesizes existing art forms into one perfect work. The interesting affair is they actually succeeded: Bauhaus was i of the key driving forces behind the popularization of the modernist way.
The term "graphic blueprint" appears for the showtime time – 1922
In his article "New Kind of Press Calls for New Design" (printed in the Boston Evening Transcript, August 29, 1922), book designer William Addison Dwiggins first used the term "graphic blueprint" to describe exactly what his function was in structuring and managing the visuals in book design. From twenty-four hour period i, designers were struggling to explain to non-designers what, exactly, they did.
Paul Rand publishes Thoughts on Design – 1947
With one foot in modernism and the other in postal service-modernism, legendary designer Paul Rand helped lead graphic pattern into its current course. He posted his theories and ideologies in the seminal work Thoughts on Pattern, which largely shaped the future of the entire graphic pattern manufacture.

His book candidly explains his design philosophies he used throughout the latter half of the twentieth century, namely a call for "functional-aesthetic perfection," an ideal residuum betwixt a logo looking proficient and communicating its points finer, seen in his popular logo designs for brands like Ford, Westinghouse, Yale, ABC, UPS, and IBM.
A glimpse into the digital era
—
From the 1950s onward, the world began its slow approach to the digital era nosotros're currently enjoying. The mass-adoption of dwelling computers is a technological advancement comparable to the invention of the printing printing, ushering in a new historic period for mass advice and granting access to esoteric fine art styles and digital software for new methods of creating art.

Adobe Photoshop—first released in 1990—fifty-fifty on its ain changed the face of graphic blueprint. Photo manipulation created a whole new subcategory of graphic pattern, blending together elements of photography, illustration, and CGI (information technology would accept made the Gesamtkunstwerk artists proud).
Simultaneously, the nature of branding also evolved to run into the irresolute times. We partially have MTV to thank for this—they brought a fresh new take on logo usage, particularly in constantly changing theirs while retaining recognizable characteristics.

When the net came into prominence effectually the turn of the century, designers took a folio out of MTV'due south volume and adopted youthful and at times edgy designs to draw the younger generation into the earth broad spider web. This can exist seen in online trends like flat design, which incorporates brilliant colors and cartoonish figures.

The history of graphic pattern is ongoing
—
That pretty much brings us upwardly to appointment with graphic design, just one area withal remains a mystery: what is the future of graphic design?
The progression of visual advice from cave paintings to digital software tin can serve as cracking inspiration, just what fruit that bears is up to you, whether yous're the adjacent generation of designer or the client whose brand might lend itself to a new spring in blueprint thinking. Though today the procedure is hard work, tough feedback, countless late nights in front of a glowing screen, the issue might merely bring about the Bauhaus or Thoughts on Design of tomorrow…
Desire to explore amazing designs and designers?
Scan a wide range of amazing designer portfolios and notice the right one for your adjacent project.
Source: https://99designs.com/blog/design-history-movements/history-graphic-design/
0 Response to "Important Events in Art From 1000 Ad to 1600 Ad Important Markings of Art in 1000 Ad"
Post a Comment